Crafting Effective Pest Treatments: Customized Strategies for Success

Pest management professionals achieve effective pest treatments through understanding pest behaviors…….
Pest Treatment Solutions: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction:
Pests are unwanted organisms that can cause damage to crops, spread diseases, contaminate food supplies, and compromise the structural integrity of buildings. Effective pest treatment solutions are critical for maintaining agricultural productivity, public health, and safety in structures. This article delves into the multifaceted world of pest management, exploring its significance, historical context, and the latest advancements in pest control strategies. Readers will gain a thorough understanding of how these solutions impact global economies, the environment, and society at large.
Understanding Pest Treatment Solutions:
Pest treatment solutions encompass a variety of methods designed to manage or eliminate pests. These solutions are a blend of biological, chemical, physical, and integrated approaches, each with its own set of applications and limitations. The core components include monitoring, identification, prevention, and control measures tailored to the specific type of pest and the environment in which it exists. Historically, pest management has evolved from reliance on organic methods to the introduction of synthetic chemicals, and now towards more sustainable and ecologically sound practices.
Global Impact and Trends:
The global impact of pests is profound, with billions of dollars lost annually in agriculture due to pest damage. Climate change has altered pest patterns, leading to new challenges and the need for innovative solutions. In tropical regions, pests like locusts and crop-destroying beetles are becoming more prevalent, while in temperate zones, invasive species continue to threaten biodiversity and agriculture. Trends indicate a growing focus on integrated pest management (IPM) systems that combine multiple tactics for effective pest control with minimal environmental impact.
Economic Considerations:
The economic aspects of pest treatment solutions are multifaceted, influencing markets, investment patterns, and overall economic health. The agricultural sector’s reliance on these solutions is significant, as they protect crops and ensure yield quality. Investment in research and development for safer and more effective treatments can lead to increased productivity and profitability. In urban settings, pest treatment solutions contribute to the maintenance of public health and safety, further impacting real estate values and consumer confidence.
Technological Advancements:
Recent technological advancements have revolutionized pest treatment solutions, leading to more precise, efficient, and environmentally friendly methods. Innovations such as drones for monitoring crops, biotechnology to create genetically modified organisms (GMOs) resistant to pests, and advanced data analytics for predictive modeling are transforming the industry. These advancements not only improve pest control but also contribute to sustainable agriculture practices.
Policy and Regulation:
The governance of pest treatment solutions is shaped by a complex web of policies and regulations that aim to protect human health, the environment, and economic interests. International bodies like the FAO and WHO set global standards for safe pesticide use, while national governments enforce their own regulations. These frameworks are critical in ensuring that pest control measures do not pose unacceptable risks to ecosystems or human well-being.
Challenges and Criticisms:
Pest treatment solutions face numerous challenges, including resistance development in pests, environmental concerns, and social and economic disparities. Critics argue that over-reliance on synthetic chemicals can harm non-target species and contribute to the decline of biodiversity. To address these issues, there is a push towards more sustainable practices, such as organic farming methods, and the use of natural predators or biological control agents.
Case Studies:
Several case studies illustrate successful applications of pest treatment solutions. One notable example is the eradication of the Mediterranean fruit fly in California using a combination of strategies including sterile insect technique (SIT). Another case involves the successful use of genetically modified crops to resist pests, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. These studies provide valuable insights into effective pest management and highlight the importance of collaboration between scientists, farmers, and policymakers.
Future Prospects:
The future of pest treatment solutions is one of continued evolution, with a focus on sustainable practices that protect both human health and the environment. Growth areas include the development of smart pest management systems, the use of beneficial microorganisms, and the integration of biological and ecological principles into control strategies. Emerging trends suggest a shift towards more holistic approaches that consider the entire ecosystem rather than targeting individual pests.
Conclusion:
Pest treatment solutions are an integral part of our global efforts to protect food security, public health, and biodiversity. Through a combination of technological innovation, sustainable practices, and effective policies, we can manage pests while minimizing environmental impact. The future of pest management is promising, with ongoing research and development poised to deliver new solutions that balance the need for protection with the imperative for ecological stewardship.
FAQ Section:
What are pest treatment solutions?
Pest treatment solutions are a variety of methods and strategies used to manage or eliminate unwanted organisms, such as insects, rodents, weeds, and fungi, that can cause harm to agriculture, human health, and the built environment.
Why are pest treatment solutions important?
Pest treatment solutions are crucial for safeguarding food security, public health, and biodiversity. They help prevent economic losses in agriculture, protect structures from damage, and maintain human well-being by minimizing exposure to harmful organisms.
What are some sustainable pest management practices?
Sustainable pest management practices include biological control, integrated pest management (IPM), organic farming methods, and the use of resistant crop varieties. These methods focus on long-term prevention and control while minimizing environmental impact.
How do technological advancements affect pest treatment solutions?
Technological advancements in pest treatment solutions include the development of precision agriculture tools, biotechnology for GMOs, data analytics for predictive modeling, and drones for crop monitoring. These technologies enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of pest control measures.
What role do policies play in pest management?
Policies establish guidelines for safe pesticide use, protect endangered species, and ensure that pest management practices are environmentally sustainable. They are essential for harmonizing the various interests at stake, including economic, environmental, and social considerations.

Pest management professionals achieve effective pest treatments through understanding pest behaviors…….

Traditional chemical cockroach treatments pose health risks and contribute to environmental damage……..

In an era focused on sustainability, ethical cockroach treatment services are vital for public healt…….

Adopting eco-friendly pest control is crucial for preserving biodiversity, reducing chemical polluti…….
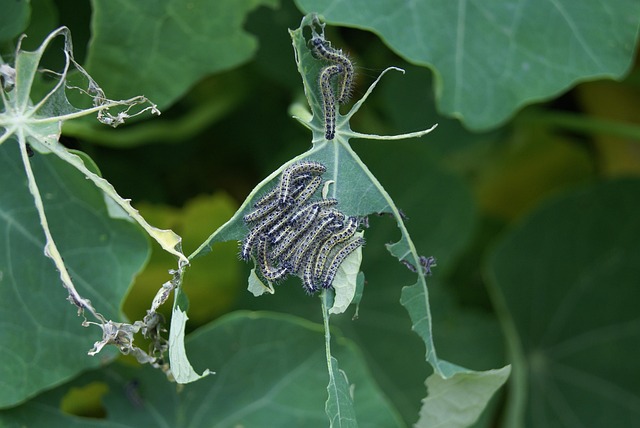

The pest control industry has undergone a significant transformation, adopting advanced technologies…….
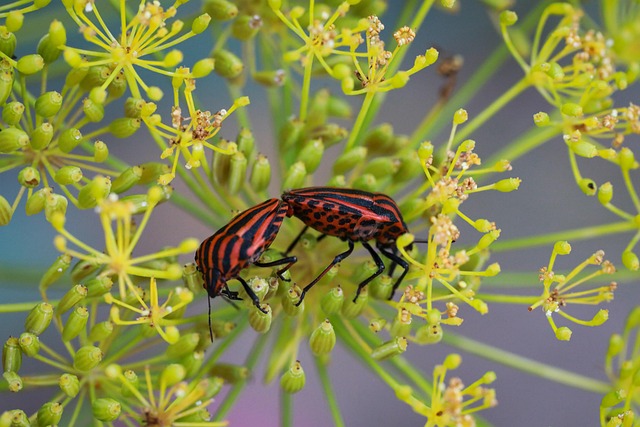

Termites, tiny but destructive, pose significant risks to homes. Professional pest control offers ef…….
Pest infestations from rodents, ants, and cockroaches require tailored bed bug treatment options due…….